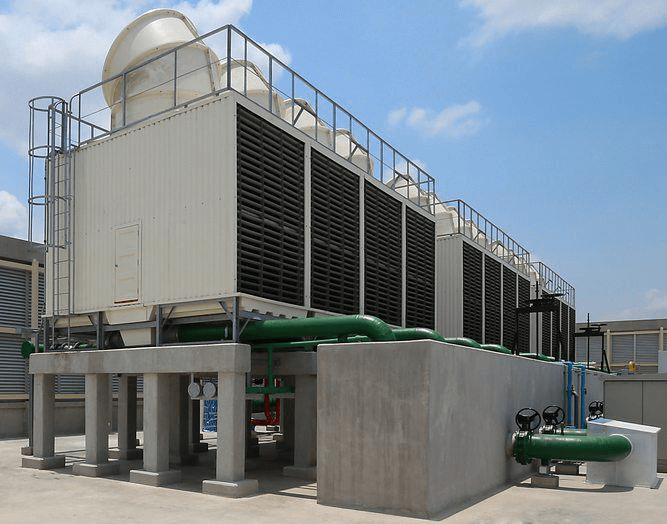
Cooling tower is a peripheral equipment that removes heat from the hot water that is pumped from the condenser to the tower. It is done by using the air from the surrounding to reduce the temperature of the water. The air can be natural or forced by the use of fan. The capacity to cool the water depends on the evaporation of the water when air comes in contact with the water.
This depends on the humidity of the surrounding air. Usually the tower should be able to cool the water by about 6°F to 7°F of the air wet bulb temperature. For example, if the wet bulb temperature of the air is 78°F and the hot water coming to the tower from the condenser is 95°F, then the cooled water that leaves the tower can be 85°F, about 7°F lower than the air wet bulb temperature.
An example of the application is the use of this equipment to cool the water-cooled condenser from a chiller system. The hot water from the chiller condenser which could be located in the building is piped to the cooling tower. Pumps are used to circulate the water from the condenser to the tower and back. The hot water is sprayed through nozzle onto the thin films materials (also known as fill) which can be made of plastic, wood slats or metal fins. Their surfaces can be in the shape of honeycomb, corrugated sheet or flat sheet.
As the water flows through these materials, air from the surrounding which can be natural-draft or forced-draft rushed through it and in the process evaporates some of it. This cools the water which is then collected at the lower sump and through a filter to get rid of leaves and other materials before being circulated back to the condenser. A drain is used to remove the hard water minerals from the system. As the amount of water will reduce due to evaporation and draining, a float valve is used to add the water to the system. The tower should be located in an area where the ventilation is good and not located too close to the building. This is critical for the natural-draft tower where the cooling is done naturally.
Cooling towers are generally classified as cooling tower by build, cooling tower by heat transfer methods and cooling tower by airflow generation methods.
1. Package type: Package type cooling towers are pre-fabricated. The shell is usually made of corrosion-free, heat resistant and durable material like fiberglass-reinforced polyester. Since they are pre-assembled, they can be easily transported to a facility of choice. Since they are compact, they are preferred in facilities with low heat rejection requirements like hospitals, malls, and office buildings.
2. Field erection type: These are large units that are generally used in power plants, huge manufacturing facilities such as steel processing plants or oil refineries. They are large structures compared to the package type. They can be manufactured according to custom specifications.
1. Dry cooling towers: Dry cooling towers operate by transferring heat through a surface that separates the working fluid from ambient air. This operates on the principle of heat transfer by a heat exchanger with extended fins. The fan is driven by an electric motor. Hence, dry cooling towers don’t consume any water.
2. Wet cooling towers or Open Circuit cooling towers: These are the most popular cooling towers because they are cost-effective and renewable. They use water to cool the facility and the heat transfer is measured by the decrease in the process temperature and a corresponding increase in both the moisture content and the wet bulb temperature of the air passing through the cooling tower.
3. Fluid cooling towers or closed circuit cooling towers: In closed circuit cooling towers, often water is mixed with glycol to form a fluid. This fluid circulates in a coil throughout the tower and is not directly exposed to the air. They are typically used where the surface needs to be clean and free of contaminants. The advantage is that there is no scale formation and hence makes for better productivity and lesser downtime.
1. Natural Draft cooling towers use the design and shape of the tower itself to move up the air naturally using fans. They use the law of different densities between ambient air and the warm air in the tower. Hence, these towers are tall to induce the airflow and are shaped like a “hyperbola”. They are typically located outside the buildings to allow for air flow.
2. Mechanical Draft towers tend to use a fan to force the air. Propeller or centrifugal fans are used to circulate air inside the tower. These are much smaller in structure than natural draft towers. Capacity control is easy in these types of towers since the speed of the fan can be controlled. Unlike natural draft towers, these can be located anywhere inside the building.
3 Cross Flow cooling towers are structured to allow air to flow horizontally while the water flows down vertically. This is done through open trough systems in the fan deck, fitted with nozzles. Since the airflow contact time is lesser, more air is required for heat transfer to occur. This type of cooling tower has many disadvantages such as higher power consumption due to the airflow required; maintenance is time consuming and is susceptible to scaling and clogging of openings.
4. Counter flow uses hot water that enters at the top, while the air is introduced at the bottom and exits at the top. Both forced and induced draft fans are used. The distribution is done through channel with lateral pipes, fitted with splash spray nozzles. Growth of algae is highly restricted, as the lateral pipes are a closed unit and not located in direct sunlight. Their power consumption is lower than cross flow units and offers the advantage of easy maintenance.
We have all these types of cooling towers ready for installation ,call us today for more information or for a quotation request.